📄 expo/modules/native-view-tutorial
File: native-view-tutorial.md | Updated: 11/15/2025
Source: https://docs.expo.dev/modules/native-view-tutorial
Hide navigation
Search
Ctrl K
Home Guides EAS Reference Learn
Archive Expo Snack Discord and Forums Newsletter
Tutorial: Create a native view
Copy page
A tutorial on creating a native view that renders a WebView with Expo Modules API.
Copy page
In this tutorial, you'll build an example module with a native view that renders a WebView. For Android, you'll use the WebView
component, and for iOS, WKWebView
. Web support can be implemented using an iframe
and is left as an exercise for you.
1
Create a new module by running the following command and name the example module expo-web-view:
Terminal
Copy
- npx create-expo-module expo-web-view
Since this is an example library and won't be published, press return for all prompts to accept the default values.
2
Clean up the default module to start with a clean slate by deleting the following files:
Terminal
Copy
- cd expo-web-view
- rm src/ExpoWebView.types.ts src/ExpoWebViewModule.ts
- rm src/ExpoWebView.web.tsx src/ExpoWebViewModule.web.ts
Locate the following files and replace them with the provided minimal boilerplate:
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/webview/ExpoWebViewModule.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.webview import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.Module import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.ModuleDefinition class ExpoWebViewModule : Module() { override fun definition() = ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView::class) {} } }
ios/ExpoWebViewModule.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore public class ExpoWebViewModule: Module { public func definition() -> ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView.self) {} } }
src/ExpoWebView.tsx
Copy
import { ViewProps } from 'react-native'; import { requireNativeViewManager } from 'expo-modules-core'; import * as React from 'react'; export type Props = ViewProps; const NativeView: React.ComponentType<Props> = requireNativeViewManager('ExpoWebView'); export default function ExpoWebView(props: Props) { return <NativeView {...props} />; }
src/index.ts
Copy
export { default as WebView, Props as WebViewProps } from './ExpoWebView';
example/App.tsx
Copy
import { WebView } from 'expo-web-view'; export default function App() { return <WebView style={{ flex: 1, backgroundColor: 'purple' }} />; }
3
To ensure everything is working, start the TypeScript compiler to watch for changes and rebuild the module's JavaScript:
Terminal
Copy
# Run this in the root of the project to start the TypeScript compiler
- npm run build
Terminal
# Navigate to the example directory
- cd example
# Run the example app on Android
- npx expo run:android
# Run the example app on iOS
- npx expo run:ios
You should now see a blank purple screen. While it's not very exciting, it's a good start. Next, turn it into a WebView.
4
Add the system WebView as a subview
Add the system WebView with a hardcoded URL as a subview of ExpoWebView. The ExpoWebView class extends ExpoView, which extends RCTView from React Native, and eventually extends View on Android and UIView on iOS.
Ensure that the WebView subview uses the same layout as ExpoWebView, whose layout is calculated by React Native's layout engine.
Android view
On Android, use LayoutParams to set the WebView's layout to match the ExpoWebView layout. You can do this when you instantiate the WebView.
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/webview/ExpoWebView.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.webview import android.content.Context import android.webkit.WebView import android.webkit.WebViewClient import expo.modules.kotlin.AppContext import expo.modules.kotlin.views.ExpoView class ExpoWebView(context: Context, appContext: AppContext) : ExpoView(context, appContext) { internal val webView = WebView(context).also { it.layoutParams = LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) it.webViewClient = object : WebViewClient() {} addView(it) it.loadUrl("https://docs.expo.dev/modules/") } }
iOS view
On iOS, set clipsToBounds to true and ensure the WebView's frame matches the bounds of ExpoWebView in layoutSubviews. The init method is called when the view is created, and layoutSubviews is called when the layout changes.
ios/ExpoWebView.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore import WebKit class ExpoWebView: ExpoView { let webView = WKWebView() required init(appContext: AppContext? = nil) { super.init(appContext: appContext) clipsToBounds = true addSubview(webView) let url = URL(string:"https://docs.expo.dev/modules/")! let urlRequest = URLRequest(url:url) webView.load(urlRequest) } override func layoutSubviews() { webView.frame = bounds } }
Show More
Example app
No changes are required. Rebuild and run the app using the following commands:
Terminal
# Prebuild the example app with the --clean flag to ensure a clean build
- npx expo prebuild --clean
# Run the example app on Android
- npx expo run:android
# Run the example app on iOS
- npx expo run:ios
After that, you'll see the Expo Modules API overview page rendered. If the changes aren't reflected, try reinstalling the app.
5
To set a prop on the view, define the prop name and setter inside ExpoWebViewModule. In this case, you can access the webView property directly for convenience. However, in real-world scenarios, keep the logic inside the ExpoWebView class to minimize how much ExpoWebViewModule knows about its internals.
Use the Prop definition component
to define the prop. In the prop setter block, you can access both the view and the prop. Specify that the URL is of type URL — the Expo modules API will convert strings to the native URL type.
Android module
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/webview/ExpoWebViewModule.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.webview import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.Module import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.ModuleDefinition import java.net.URL class ExpoWebViewModule : Module() { override fun definition() = ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView::class) { Prop("url") { view: ExpoWebView, url: URL? -> view.webView.loadUrl(url.toString()) } } } }
iOS module
ios/ExpoWebViewModule.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore public class ExpoWebViewModule: Module { public func definition() -> ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView.self) { Prop("url") { (view, url: URL) in if view.webView.url != url { let urlRequest = URLRequest(url: url) view.webView.load(urlRequest) } } } } }
TypeScript module
Next, add the url prop to the Props type.
src/ExpoWebView.tsx
Copy
import { ViewProps } from 'react-native'; import { requireNativeViewManager } from 'expo-modules-core'; import * as React from 'react'; export type Props = { url?: string; } & ViewProps; const NativeView: React.ComponentType<Props> = requireNativeViewManager('ExpoWebView'); export default function ExpoWebView(props: Props) { return <NativeView {...props} />; }
Example app
Finally, pass a URL to your WebView component in the example app.
example/App.tsx
Copy
import { WebView } from 'expo-web-view'; export default function App() { return <WebView style={{ flex: 1 }} url="https://expo.dev" />; }
Rebuild the example app:
Terminal
- npx expo prebuild --clean
# Run the example app on Android
- npx expo run:android
# Run the example app on iOS
- npx expo run:ios
After that, you'll see the Expo homepage in the WebView.
6
Add an event to notify when the page has loaded
View callbacks
allow developers to listen for events on components. They are typically registered through props on the component, for example: <Image onLoad={...} />. Use the Events definition component
to define an event for your WebView. Call it onLoad.
Android view and module
On Android, override the onPageFinished function. Then, call the onLoad event handler that you defined in the module.
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/webview/ExpoWebView.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.webview import android.content.Context import android.webkit.WebView import android.webkit.WebViewClient import expo.modules.kotlin.AppContext import expo.modules.kotlin.viewevent.EventDispatcher import expo.modules.kotlin.views.ExpoView class ExpoWebView(context: Context, appContext: AppContext) : ExpoView(context, appContext) { private val onLoad by EventDispatcher() internal val webView = WebView(context).also { it.layoutParams = LayoutParams( LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ) it.webViewClient = object : WebViewClient() { override fun onPageFinished(view: WebView, url: String) { onLoad(mapOf("url" to url)) } } addView(it) } }
Show More
Indicate in ExpoWebViewModule that the View has an onLoad event.
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/webview/ExpoWebViewModule.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.webview import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.Module import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.ModuleDefinition import java.net.URL class ExpoWebViewModule : Module() { override fun definition() = ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView::class) { Events("onLoad") Prop("url") { view: ExpoWebView, url: URL? -> view.webView.loadUrl(url.toString()) } } } }
Show More
iOS view and module
On iOS, implement webView(_:didFinish:) and make ExpoWebView extend WKNavigationDelegate. Then, call onLoad from that delegate method.
ios/ExpoWebView.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore import WebKit class ExpoWebView: ExpoView, WKNavigationDelegate { let webView = WKWebView() let onLoad = EventDispatcher() required init(appContext: AppContext? = nil) { super.init(appContext: appContext) clipsToBounds = true webView.navigationDelegate = self addSubview(webView) } override func layoutSubviews() { webView.frame = bounds } func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didFinish navigation: WKNavigation!) { if let url = webView.url { onLoad([ "url": url.absoluteString ]) } } }
Show More
Indicate in ExpoWebViewModule that the View has an onLoad event.
ios/ExpoWebViewModule.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore public class ExpoWebViewModule: Module { public func definition() -> ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoWebView") View(ExpoWebView.self) { Events("onLoad") Prop("url") { (view, url: URL) in if view.webView.url != url { let urlRequest = URLRequest(url: url) view.webView.load(urlRequest) } } } } }
Show More
TypeScript module
Event payloads are included within the nativeEvent property of the event. To access the url from the onLoad event, read event.nativeEvent.url.
src/ExpoWebView.tsx
Copy
import { ViewProps } from 'react-native'; import { requireNativeViewManager } from 'expo-modules-core'; import * as React from 'react'; export type OnLoadEvent = { url: string; }; export type Props = { url?: string; onLoad?: (event: { nativeEvent: OnLoadEvent }) => void; } & ViewProps; const NativeView: React.ComponentType<Props> = requireNativeViewManager('ExpoWebView'); export default function ExpoWebView(props: Props) { return <NativeView {...props} />; }
Show More
Example app
Update the example app to show an alert when the page has loaded. Copy the following code, then rebuild and run your app, and you'll see the alert!
example/App.tsx
Copy
import { WebView } from 'expo-web-view'; export default function App() { return ( <WebView style={{ flex: 1 }} url="https://expo.dev" onLoad={event => alert(`loaded ${event.nativeEvent.url}`)} /> ); }
7
Bonus: Build a web browser UI around it
Now that you have a WebView, build a web browser UI around it. Try rebuilding a browser UI, and feel free to add new native capabilities as needed (for example, support for back or reload buttons). If you need inspiration, see the example below.
App.tsx
Copy
import { useState } from 'react'; import { ActivityIndicator, Platform, Text, TextInput, View } from 'react-native'; import { WebView } from 'expo-web-view'; export default function App() { const [inputUrl, setInputUrl] = useState('https://docs.expo.dev/modules/'); const [url, setUrl] = useState(inputUrl); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true); return ( <View style={{ flex: 1, paddingTop: Platform.OS === 'ios' ? 80 : 30 }}> <TextInput value={inputUrl} onChangeText={setInputUrl} returnKeyType="go" autoCapitalize="none" onSubmitEditing={() => { if (inputUrl !== url) { setUrl(inputUrl); setIsLoading(true); } }} keyboardType="url" style={{ color: '#fff', backgroundColor: '#000', borderRadius: 10, marginHorizontal: 10, paddingHorizontal: 20, height: 60, }} /> <WebView url={url.startsWith('https://') || url.startsWith('http://') ? url : `https://${url}`} onLoad={() => setIsLoading(false)} style={{ flex: 1, marginTop: 20 }} /> <LoadingView isLoading={isLoading} /> </View> ); } function LoadingView({ isLoading }: { isLoading: boolean }) { if (!isLoading) { return null; } return ( <View style={{ position: 'absolute', bottom: 0, left: 0, right: 0, height: 80, backgroundColor: 'rgba(0,0,0,0.5)', paddingBottom: 10, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', flexDirection: 'row', }}> <ActivityIndicator animating={isLoading} color="#fff" style={{ marginRight: 10 }} /> <Text style={{ color: '#fff' }}>Loading...</Text> </View> ); }
Show More
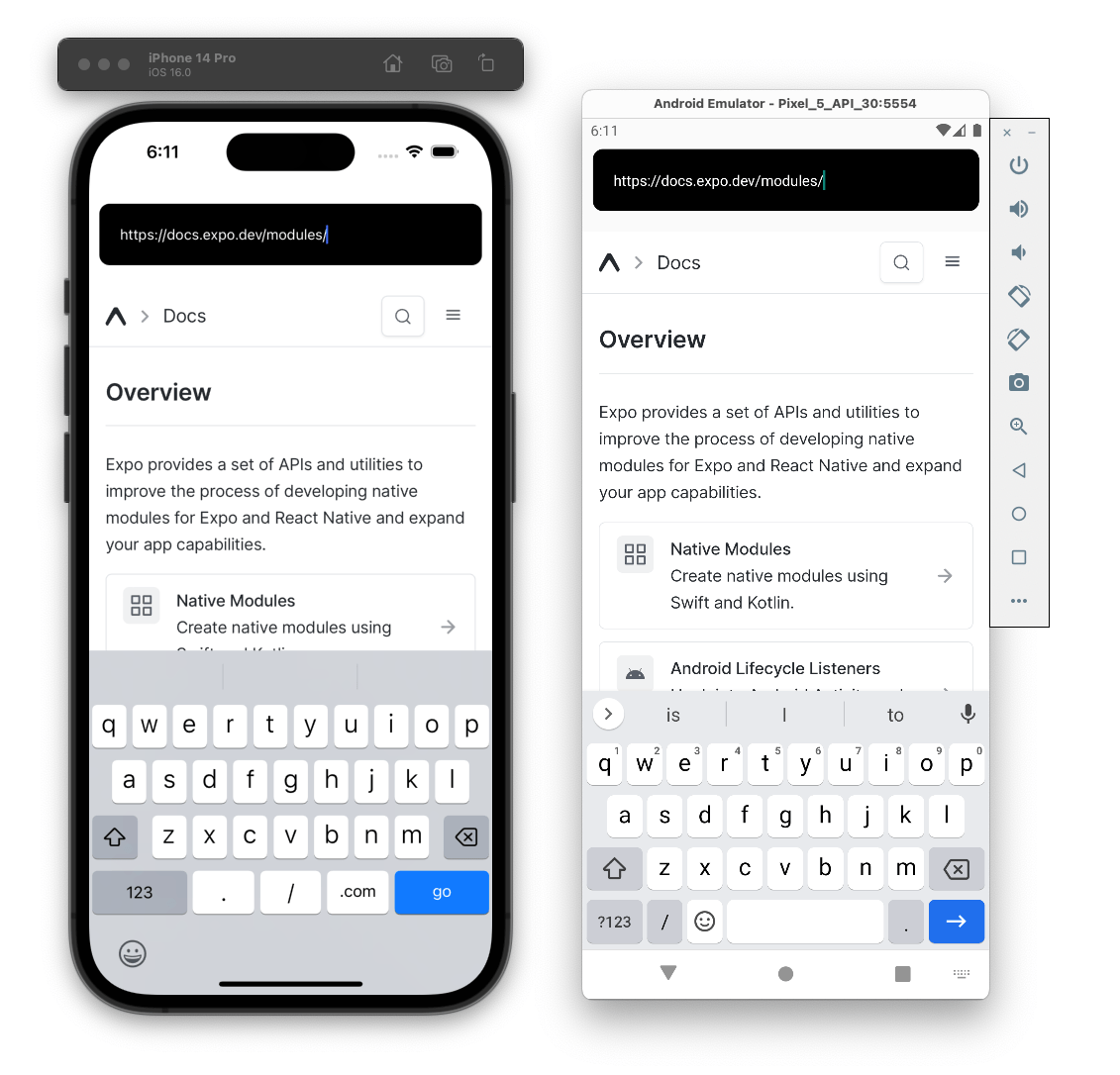
Congratulations! You've created your first Expo module with a native view for Android and iOS.
Expo Modules API Reference
Create native modules using Kotlin and Swift.
Tutorial: Creating a native module
A tutorial on creating a native module that persists settings with Expo Modules API.