📄 expo/modules/third-party-library
File: third-party-library.md | Updated: 11/15/2025
Source: https://docs.expo.dev/modules/third-party-library
Hide navigation
Search
Ctrl K
Home Guides EAS Reference Learn
Archive Expo Snack Discord and Forums Newsletter
Wrap third-party native libraries
Copy page
Learn how to create a simple wrapper around two separate native libraries using Expo Modules API.
Copy page
Expo modules make it possible to easily use native, external libraries built for Android and iOS in React Native projects. This tutorial focuses on utilizing the Expo Modules API to create radial charts using two similar libraries accessible on both native platforms.
The iOS library is inspired by the Android library, so they both have similar API and functionality. This makes them a good example for this tutorial.
1
The following steps assume that the new module is created inside a new Expo project. However, you can create a new module inside an existing project by following the alternative instructions.
In an existing Expo project
Start with a new module
Alternatively, you can use the new module as a view inside the existing Expo project directory. Run the following command in your project's directory:
Terminal
Copy
- npx create-expo-module --local expo-radial-chart
Now, open the newly created modules/expo-radial-chart directory to start editing the native code.
Create a new empty Expo module that can be published on npm and utilized in any Expo app by running the following command:
Terminal
Copy
- npx create-expo-module expo-radial-chart
Tip: If you aren't going to ship this library, press return for all the prompts to accept the default values in the terminal window.
Now, open the newly created expo-radial-chart directory to start editing the native code.
2
To verify that everything is functioning correctly, let's run the example project.
In an existing Expo project
In a new module
If you started with an existing Expo project, run the following commands from your Expo project's root directory:
Terminal
# Run the example-expo-app on Android
- npx expo run:android
# Run the example app on iOS
- npx expo run:ios
If you started with a new module project, open a terminal window, start the TypeScript compiler to watch for changes, and rebuild the module JavaScript:
Terminal
Copy
# Ensure you are inside expo-radial-chart directory before running the command below
- npm run build
In another terminal window, compile and run the example app:
Terminal
- cd example-expo-app
# Run the example-expo-app on Android
- npx expo run:android
# Run the example app on iOS
- npx expo run:ios
3
Add the native dependencies to the module by editing the expo-radial-chart/android/build.gradle and expo-radial-chart/ios/ExpoRadialChart.podspec files:
android/build.gradle
Copy
dependencies { implementation project(':expo-modules-core') implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:${getKotlinVersion()}" + implementation 'com.github.PhilJay:MPAndroidChart:v3.1.0' }
ios/ExpoRadialChart.podspec
Copy
s.static_framework = true s.dependency 'ExpoModulesCore' + s.dependency 'DGCharts', '~> 5.1.0' # Swift/Objective-C compatibility
Are you trying to use a .aar dependency?
SDK 52 and later
SDK 51 and earlier
Inside the android directory, create another directory called libs and place the .aar file inside it. Then, add the file as a Gradle project from autolinking:
expo-module.config.json
Copy
`"android": { + "gradleAarProjects": [ + { + "name": "test-aar", + "aarFilePath": "android/libs/test.aar" + } + ], "modules": [`\
Finally, add the dependency to the dependencies list in the android/build.gradle file, using the dependency's specified name with ${project.name}$ prefix:
android/build.gradle
Copy
dependencies { implementation project(':expo-modules-core') implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:${getKotlinVersion()}" + implementation project(":${project.name}\$test-aar") }
Inside the android directory, create another directory called libs and place the .aar file inside it. Then, add the directory as a repository:
android/build.gradle
Copy
repositories { mavenCentral() + flatDir { + dirs 'libs' + } }
Finally, add the dependency to the dependencies list. Instead of the filename, use the package path, which includes the @aar at the end:
android/build.gradle
Copy
dependencies { implementation project(':expo-modules-core') implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:${getKotlinVersion()}" + implementation 'com.github.PhilJay:MPAndroidChart:v3.1.0@aar' }
Are you trying to use an .xcframework or .framework dependency?
On iOS, you can also use dependencies bundled as a framework by using the vendored_frameworks config option.
ios/ExpoRadialChart.podspec
Copy
s.static_framework = true s.dependency 'ExpoModulesCore' + s.vendored_frameworks = 'Frameworks/MyFramework.framework' # Swift/Objective-C compatibility
\
Note: The file pattern used to specify the path to the framework is relative to the podspec file, and doesn't support traversing the parent directory (
..), meaning you need to place the framework inside the ios directory (or a subdirectory of ios).
Once the framework is added, make sure that thesource_filesoption file pattern doesn't match any files inside the framework. One way to achieve this is to move your iOS source Swift files (that isExpoRadialChartView.swiftandExpoRadialChartModule.swift) into a src directory separate from where you placed your framework(s) and update thesource_filesoption to only match the src directory:
ios/ExpoRadialChart.podspec
Copy
- s.source_files = '**/*.{h,m,mm,swift,hpp,cpp}' + s.source_files = 'src/**/*.{h,m,mm,swift,hpp,cpp}'
Your ios directory should end up with a file structure similar to this:
Frameworks
MyFramework.framework
src
ExpoRadialChartView.swift
ExpoRadialChartModule.swift
ExpoRadialChart.podspec
4
Define an API
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To use the module in the app, define the types for the props. It accepts a list of series — each with a color and a percentage value.
src/ExpoRadialChart.types.ts
Copy
import { ViewStyle } from 'react-native/types'; export type ChangeEventPayload = { value: string; }; type Series = { color: string; percentage: number; }; export type ExpoRadialChartViewProps = { style?: ViewStyle; data: Series[]; };
Since the module isn't implemented for web in this example, let's replace the src/ExpoRadialChartView.web.tsx file:
src/ExpoRadialChartView.web.tsx
Copy
import * as React from 'react'; export default function ExpoRadialChartView() { return <div>Not implemented</div>; }
5
Implement the module on Android
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Now you can implement the native functionality by editing the placeholder files with the following changes:
\
- Create a
PieChartinstance and set itslayoutParamsto match the parent view. Then, add it to the view hierarchy using theaddViewfunction.\ - Define a
setChartDatafunction that accepts a list ofSeriesobjects. You can iterate over the list, create aPieEntryfor each series and store the colors in a separate list.\ - Create a
PieDataSet, use it to create aPieDataobject, and set it as data on thePieChartinstance.
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/radialchart/ExpoRadialChartView.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.radialchart import android.content.Context import android.graphics.Color import androidx.annotation.ColorInt import com.github.mikephil.charting.charts.PieChart import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.PieData import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.PieDataSet import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.PieEntry import expo.modules.kotlin.AppContext import expo.modules.kotlin.records.Field import expo.modules.kotlin.records.Record import expo.modules.kotlin.views.ExpoView class Series : Record { @Field val color: String = "#ff0000" @Field val percentage: Float = 0.0f } class ExpoRadialChartView(context: Context, appContext: AppContext) : ExpoView(context, appContext) { internal val chartView = PieChart(context).also { it.layoutParams = LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) addView(it) } fun setChartData(data: ArrayList<Series>) { val entries: ArrayList<PieEntry> = ArrayList() val colors: ArrayList<Int> = ArrayList() for (series in data) { entries.add(PieEntry(series.percentage)) colors.add(Color.parseColor(series.color)) } val dataSet = PieDataSet(entries, "DataSet"); dataSet.colors = colors; val pieData = PieData(dataSet); chartView.data = pieData; chartView.invalidate(); } }
Show More
You also need to use theProp
function to define thedataprop and call the nativesetChartDatafunction when the prop changes:
android/src/main/java/expo/modules/radialchart/ExpoRadialChartModule.kt
Copy
package expo.modules.radialchart import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.Module import expo.modules.kotlin.modules.ModuleDefinition class ExpoRadialChartModule : Module() { override fun definition() = ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoRadialChart") View(ExpoRadialChartView::class) { Prop("data") { view: ExpoRadialChartView, prop: ArrayList<Series> -> view.setChartData(prop); } } } }
6
Implement the module on iOS
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Now you can implement the native functionality by editing the placeholder files with the following changes:
\ - Create a new
PieChartViewinstance and use theaddSubviewfunction to add it to the view hierarchy.\ - Set the
clipsToBoundsproperty and override thelayoutSubviewsfunction to make sure the chart view is always the same size as the parent view.\ - Create a
setChartDatafunction that accepts a list of series, creates aPieChartDataSetinstance with the data, and assigns it to thedataproperty of thePieChartViewinstance.
ios/ExpoRadialChartView.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore import DGCharts struct Series: Record { @Field var color: UIColor = UIColor.black @Field var percentage: Double = 0 } class ExpoRadialChartView: ExpoView { let chartView = PieChartView() required init(appContext: AppContext? = nil) { super.init(appContext: appContext) clipsToBounds = true addSubview(chartView) } override func layoutSubviews() { chartView.frame = bounds } func setChartData(data: [Series]) { let set1 = PieChartDataSet(entries: data.map({ (series: Series) -> PieChartDataEntry in return PieChartDataEntry(value: series.percentage) })) set1.colors = data.map({ (series: Series) -> UIColor in return series.color }) let chartData: PieChartData = [set1] chartView.data = chartData } }
Show More
You also need to use theProp
function to define thedataprop and call the nativesetChartDatafunction when the prop changes:
ios/ExpoRadialChartModule.swift
Copy
import ExpoModulesCore public class ExpoRadialChartModule: Module { public func definition() -> ModuleDefinition { Name("ExpoRadialChart") View(ExpoRadialChartView.self) { Prop("data") { (view: ExpoRadialChartView, prop: [Series]) in view.setChartData(data: prop) } } } }
7
Write an example app to use the module
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can update the app inside the app directory to test the module. Use theExpoRadialChartViewcomponent to render a pie chart with three slices:
app/(tabs)/index.tsx
Copy
import { ExpoRadialChartView } from '@/modules/expo-radial-chart'; import { StyleSheet } from 'react-native'; export default function App() { return ( <ExpoRadialChartView style={styles.container} data={[ { color: '#ff0000', percentage: 0.5, }, { color: '#00ff00', percentage: 0.2, }, { color: '#0000ff', percentage: 0.3, }, ]} /> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, }, });
Show More
\
Tip: If you created a new module, make sure to update the import statement to:
import { ExpoRadialChartView } from 'expo-radial-chart';
8
Rebuild and launch your application
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
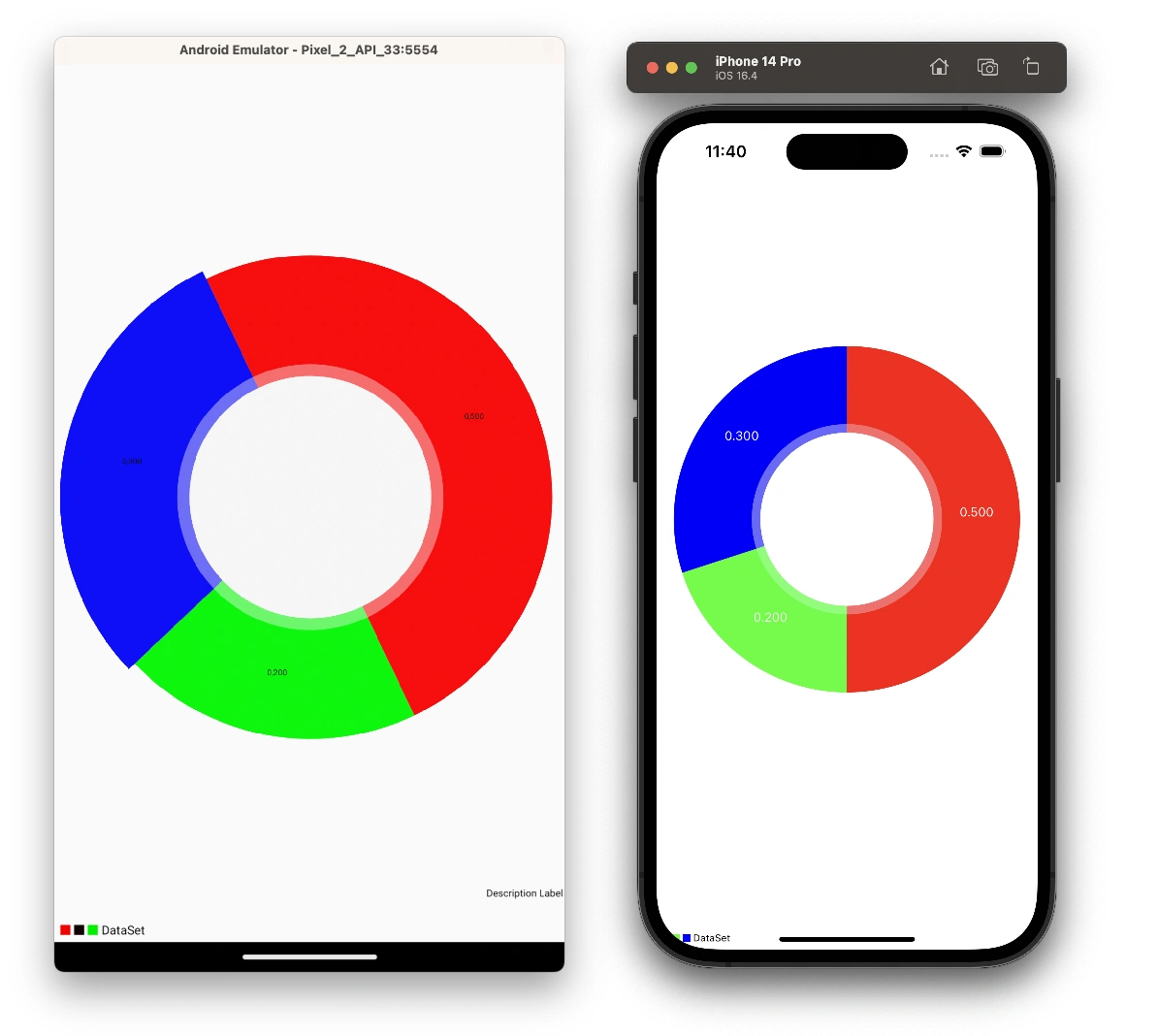
To make sure your app builds successfully on both platforms, rerun the build commands from step 2. After the app is successfully built on any of the platform you'll see a pie chart with three slices:
Congratulations! You have created your first simple wrapper around two separate third-party native libraries using Expo Modules API.
Next step
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Expo Modules API Reference
A reference to create native modules using Kotlin and Swift.