📄 tanstack/form/v1/docs/framework/solid/guides/basic-concepts
File: basic-concepts.md | Updated: 11/15/2025
Source: https://tanstack.com/form/v1/docs/framework/solid/guides/basic-concepts
Search...
+ K
Auto
Docs Examples GitHub Contributors
Docs Examples GitHub Contributors
Docs Examples GitHub Contributors
Docs Examples Github Contributors
Docs Examples Github Contributors
Docs Examples Github Contributors
Docs Examples Github Contributors
Docs Examples Github Contributors
Maintainers Partners Support Learn StatsBETA Discord Merch Blog GitHub Ethos Brand Guide
Documentation
Framework
Solid
Version
v1
Search...
+ K
Menu
Getting Started
Guides
API Reference
Examples
Framework
Solid
Version
v1
Menu
Getting Started
Guides
API Reference
Examples
On this page
Basic Concepts and Terminology
Copy Markdown
This page introduces the basic concepts and terminology used in the @tanstack/solid-form library. Familiarizing yourself with these concepts will help you better understand and work with the library.
You can create options for your form so that it can be shared between multiple forms by using the formOptions function.
Example:
tsx
const formOpts = formOptions({
defaultValues: {
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
hobbies: [],
} as Person,
})
const formOpts = formOptions({
defaultValues: {
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
hobbies: [],
} as Person,
})
A Form Instance is an object that represents an individual form and provides methods and properties for working with the form. You create a form instance using the createForm hook provided by the form options. The hook accepts an object with an onSubmit function, which is called when the form is submitted.
tsx
const form = createForm(() => ({
...formOpts,
onSubmit: async ({ value }) => {
// Do something with form data
console.log(value)
},
}))
const form = createForm(() => ({
...formOpts,
onSubmit: async ({ value }) => {
// Do something with form data
console.log(value)
},
}))
You may also create a form instance without using formOptions by using the standalone createForm API:
tsx
const form = createForm<Person>(() => ({
onSubmit: async ({ value }) => {
// Do something with form data
console.log(value)
},
defaultValues: {
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
hobbies: [],
},
}))
const form = createForm<Person>(() => ({
onSubmit: async ({ value }) => {
// Do something with form data
console.log(value)
},
defaultValues: {
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
hobbies: [],
},
}))
A Field represents a single form input element, such as a text input or a checkbox. Fields are created using the form.Field component provided by the form instance. The component accepts a name prop, which should match a key in the form's default values. It also accepts a children prop, which is a render prop function that takes a field object as its argument.
Example:
tsx
<form.Field
name="firstName"
children={(field) => (
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
)}
/>
<form.Field
name="firstName"
children={(field) => (
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
)}
/>
Each field has its own state, which includes its current value, validation status, error messages, and other metadata. You can access a field's state using the field().state property.
Example:
ts
const {
value,
meta: { errors, isValidating },
} = field().state
const {
value,
meta: { errors, isValidating },
} = field().state
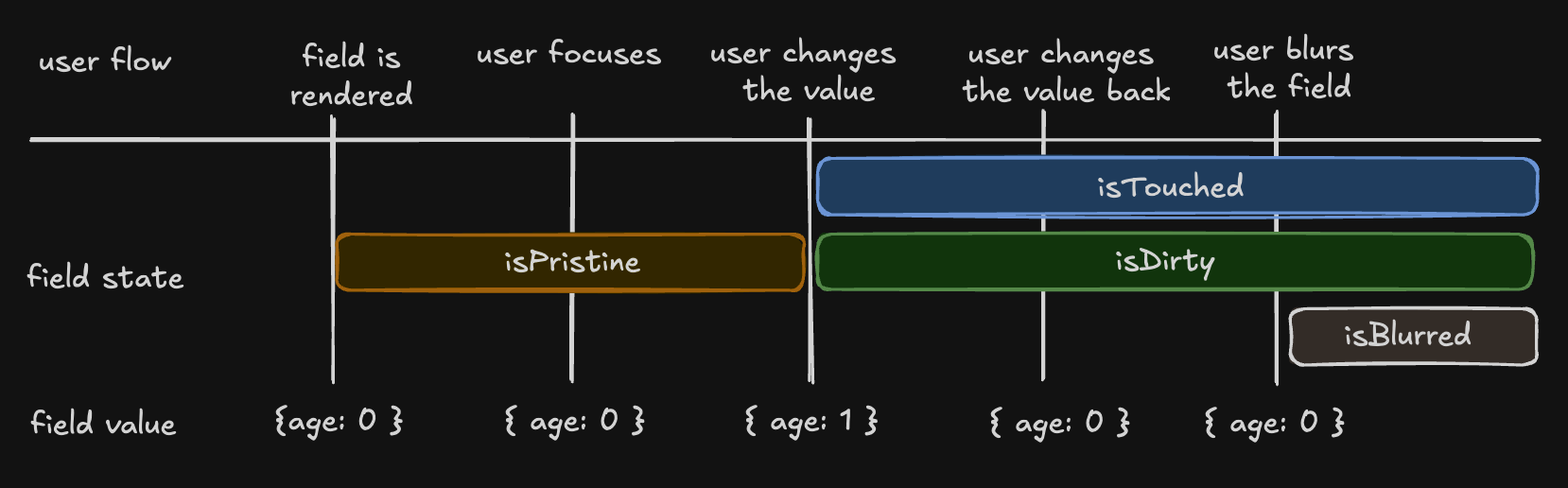
There are four states in the metadata that can be useful to see how the user interacts with a field:
- "isTouched", after the user changes the field or blurs the field
- "isDirty", after the field's value has been changed, even if it's been reverted to the default. Opposite of isPristine
- "isPristine", until the user changes the field value. Opposite of isDirty
- "isBlurred", after the field has been blurred
ts
const { isTouched, isDirty, isPristine, isBlurred } = field().state.meta
const { isTouched, isDirty, isPristine, isBlurred } = field().state.meta
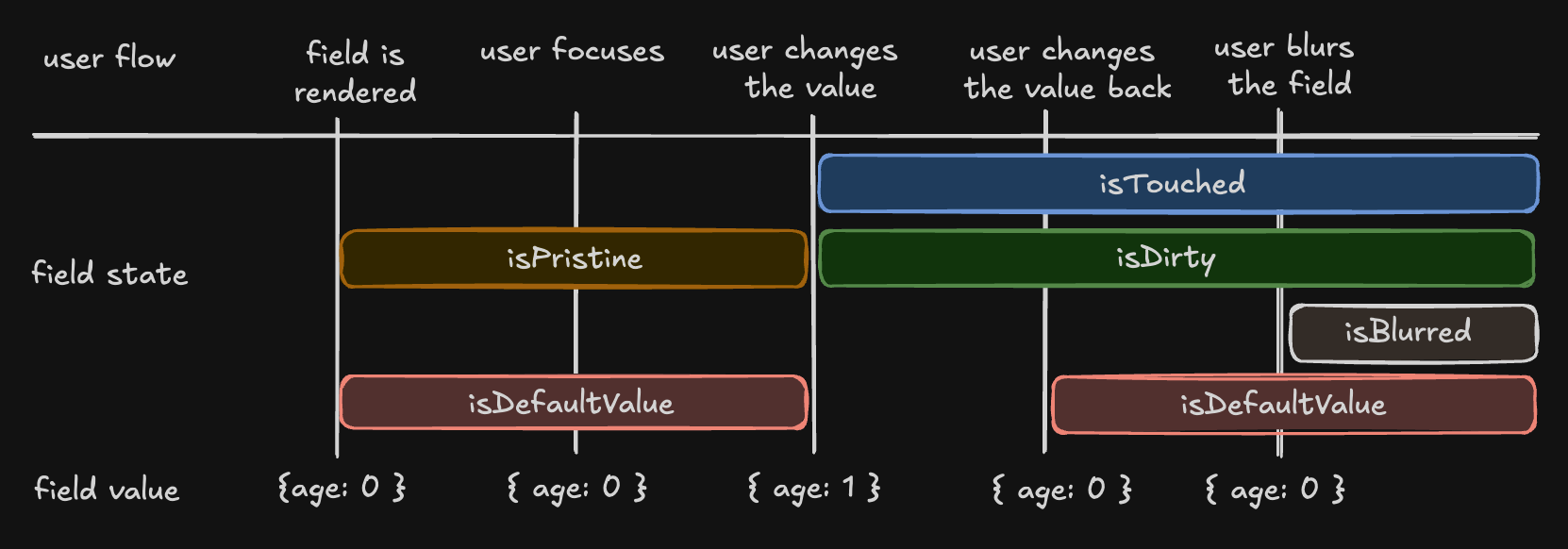
Understanding 'isDirty' in Different Libraries
----------------------------------------------
Non-Persistent dirty state
- Libraries: React Hook Form (RHF), Formik, Final Form.
- Behavior: A field is 'dirty' if its value differs from the default. Reverting to the default value makes it 'clean' again.
Persistent dirty state
- Libraries: Angular Form, Vue FormKit.
- Behavior: A field remains 'dirty' once changed, even if reverted to the default value.
We have chosen the persistent 'dirty' state model. To also support a non-persistent 'dirty' state, we introduce an additional flag:
- "isDefaultValue", whether the field's current value is the default value
ts
const { isDefaultValue, isTouched } = field().state.meta
// The following line will re-create the non-Persistent `dirty` functionality.
const nonPersistentIsDirty = !isDefaultValue
const { isDefaultValue, isTouched } = field().state.meta
// The following line will re-create the non-Persistent `dirty` functionality.
const nonPersistentIsDirty = !isDefaultValue
The Field API is an object passed to the render prop function when creating a field. It provides methods for working with the field's state.
Example:
tsx
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
@tanstack/solid-form provides both synchronous and asynchronous validation out of the box. Validation functions can be passed to the form.Field component using the validators prop.
Example:
tsx
<form.Field
name="firstName"
validators={{
onChange: ({ value }) =>
!value
? 'A first name is required'
: value.length < 3
? 'First name must be at least 3 characters'
: undefined,
onChangeAsync: async ({ value }) => {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
return value.includes('error') && 'No "error" allowed in first name'
},
}}
children={(field) => (
<>
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<p>{field().state.meta.errors[0]}</p>
</>
)}
/>
<form.Field
name="firstName"
validators={{
onChange: ({ value }) =>
!value
? 'A first name is required'
: value.length < 3
? 'First name must be at least 3 characters'
: undefined,
onChangeAsync: async ({ value }) => {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
return value.includes('error') && 'No "error" allowed in first name'
},
}}
children={(field) => (
<>
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<p>{field().state.meta.errors[0]}</p>
</>
)}
/>
Validation with Standard Schema Libraries
-----------------------------------------
In addition to hand-rolled validation options, we also support the Standard Schema specification.
You can define a schema using any of the libraries implementing the specification and pass it to a form or field validator.
Supported libraries include:
- Zod (v3.24.0 or higher)
- Valibot (v1.0.0 or higher)
- ArkType (v2.1.20 or higher)
- Yup (v1.7.0 or higher)
tsx
import { z } from 'zod'
// ...
;<form.Field
name="firstName"
validators={{
onChange: z.string().min(3, 'First name must be at least 3 characters'),
onChangeAsyncDebounceMs: 500,
onChangeAsync: z.string().refine(
async (value) => {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
return !value.includes('error')
},
{
message: 'No "error" allowed in first name',
},
),
}}
children={(field) => (
<>
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<p>{field().state.meta.errors[0]}</p>
</>
)}
/>
import { z } from 'zod'
// ...
;<form.Field
name="firstName"
validators={{
onChange: z.string().min(3, 'First name must be at least 3 characters'),
onChangeAsyncDebounceMs: 500,
onChangeAsync: z.string().refine(
async (value) => {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
return !value.includes('error')
},
{
message: 'No "error" allowed in first name',
},
),
}}
children={(field) => (
<>
<input
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<p>{field().state.meta.errors[0]}</p>
</>
)}
/>
@tanstack/solid-form offers various ways to subscribe to form and field state changes, most notably the form.useStore hook and the form.Subscribe component. These methods allow you to optimize your form's rendering performance by only updating components when necessary.
Example:
tsx
const firstName = form.useStore((state) => state.values.firstName)
//...
<form.Subscribe
selector={(state) => ({
canSubmit: state.canSubmit,
isSubmitting: state.isSubmitting,
})}
children={(state) => (
<button type="submit" disabled={!state().canSubmit}>
{state().isSubmitting ? '...' : 'Submit'}
</button>
)}
/>
const firstName = form.useStore((state) => state.values.firstName)
//...
<form.Subscribe
selector={(state) => ({
canSubmit: state.canSubmit,
isSubmitting: state.isSubmitting,
})}
children={(state) => (
<button type="submit" disabled={!state().canSubmit}>
{state().isSubmitting ? '...' : 'Submit'}
</button>
)}
/>
Array fields allow you to manage a list of values within a form, such as a list of hobbies. You can create an array field using the form.Field component with the mode="array" prop.
When working with array fields, you can use the fields pushValue, removeValue, swapValues and moveValue methods to add, remove, swap, and move a value from one index to another within the array, respectively. Additional helper methods such as insertValue, replaceValue, and clearValues are also available for inserting, replacing, and clearing array values.
Example:
tsx
<form.Field
name="hobbies"
mode="array"
children={(hobbiesField) => (
<div>
Hobbies
<div>
<Show
when={hobbiesField().state.value.length > 0}
fallback={'No hobbies found.'}
>
<Index each={hobbiesField().state.value}>
{(_, i) => (
<div>
<form.Field
name={`hobbies[${i}].name`}
children={(field) => (
<div>
<label for={field().name}>Name:</label>
<input
id={field().name}
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<button
type="button"
onClick={() => hobbiesField().removeValue(i)}
>
X
</button>
</div>
)}
/>
<form.Field
name={`hobbies[${i}].description`}
children={(field) => {
return (
<div>
<label for={field().name}>Description:</label>
<input
id={field().name}
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
</div>
)
}}
/>
</div>
)}
</Index>
</Show>
</div>
<button
type="button"
onClick={() =>
hobbiesField().pushValue({
name: '',
description: '',
yearsOfExperience: 0,
})
}
>
Add hobby
</button>
</div>
)}
/>
<form.Field
name="hobbies"
mode="array"
children={(hobbiesField) => (
<div>
Hobbies
<div>
<Show
when={hobbiesField().state.value.length > 0}
fallback={'No hobbies found.'}
>
<Index each={hobbiesField().state.value}>
{(_, i) => (
<div>
<form.Field
name={`hobbies[${i}].name`}
children={(field) => (
<div>
<label for={field().name}>Name:</label>
<input
id={field().name}
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
<button
type="button"
onClick={() => hobbiesField().removeValue(i)}
>
X
</button>
</div>
)}
/>
<form.Field
name={`hobbies[${i}].description`}
children={(field) => {
return (
<div>
<label for={field().name}>Description:</label>
<input
id={field().name}
name={field().name}
value={field().state.value}
onBlur={field().handleBlur}
onInput={(e) => field().handleChange(e.target.value)}
/>
</div>
)
}}
/>
</div>
)}
</Index>
</Show>
</div>
<button
type="button"
onClick={() =>
hobbiesField().pushValue({
name: '',
description: '',
yearsOfExperience: 0,
})
}
>
Add hobby
</button>
</div>
)}
/>
These are the basic concepts and terminology used in the @tanstack/solid-form library. Understanding these concepts will help you work more effectively with the library and create complex forms with ease.



